Special steel material purposes
- Engine
- Drive
- Axle
Production capacity
- Steel
- 310 million tons
- Product
- 280 million tons

영상이 자동 재생중이니 정지하시려면 다음의 버튼을 클릭하시기 바랍니다. Play/Stop
- 현재위치
- Products
- Process Simulation
-
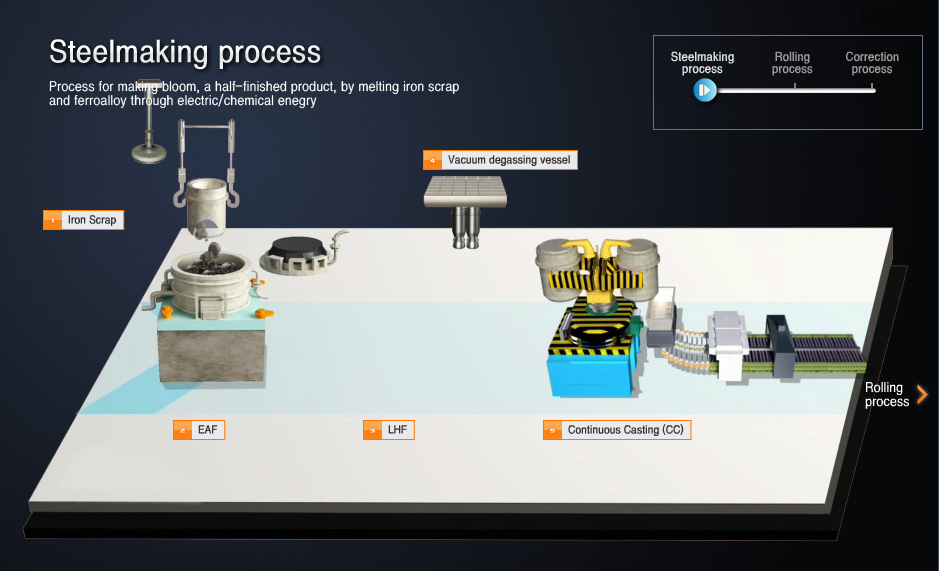
- 01Iron scrap
- Main material for electric furnace steel manufacture
Scrap metal discarded from the production or process and after the end of lifespan of finished steel products
-
- 02EAF (Electric Arc Furnace)
- Process of melting solid iron scrap into liquid metallic strain using electrical and chemical energy
- Electrical energy: thermal energy of Arc occurring between electrode and iron scrap
- Chemical energy: thermal energy occurring between oxygen and metal element
-
- 03LHF Ladle Heating Furnace
- Metallic stain produced in the electric furnace received in a vessel called ladle
- Rise in temperature using electric energy
- Adjust chemical elements through alloy metal insertion
- Process that reduces refinement through making optimum slag
-
- 04Vacuum degassing vessel
- Process of degassing hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen and etc. in metallic stain by exposing finished clean metallic stain to low vacuum state under 0.8m bar lower than atmospheric pressure
- VD: Equipment that exposes ladle with metallic stain into a vacuum state by putting it in equipment in a tank form
- RH: Equipment that exposes metallic stain in ladle to a vacuum state by reverting it into a particular vessel
-
- 05CC Continuous Casting
- Equipment that produce bloom/billet continuously by infusing melted steel in a certain form of mold
- Clean steel and high alloy steel production through M-EMS/F-EMS and dynamic soft reduction equipment
-
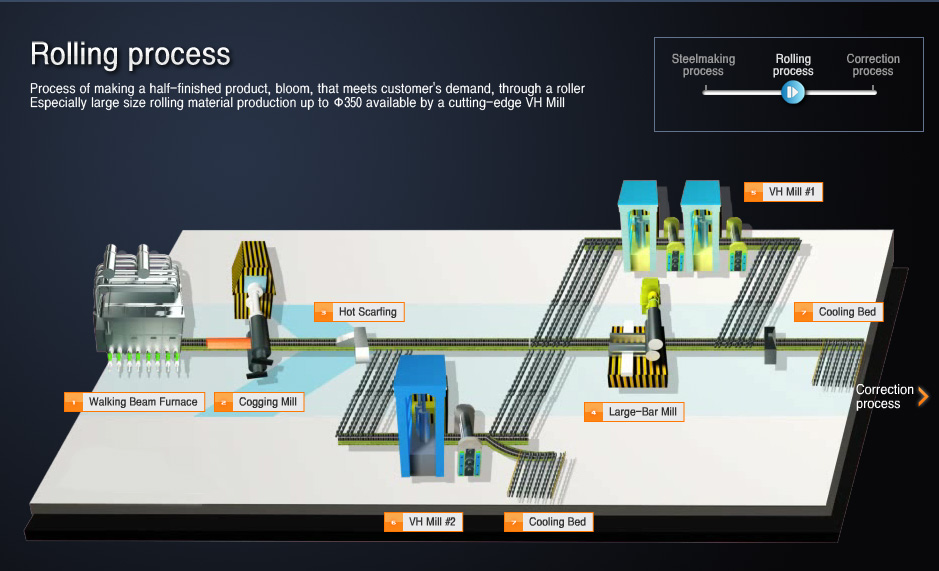
- 01Walking Beam Furnace
- Process of heating blood produced by soft mold uniformly (at approximately 1200 degrees Celsius) to facilitate plastic deformation
Characteristics
- Chemical impurity decrease in the mold structure from spread caused by high-temperature heating
- During rolling, air bladder or porosity in the steel lump disappears and coarse grains refined
-
- 02Cogging Mill (Hot rolling mill)
- Plastic deformation process which desired shape and standard are formed by reversibly rolling the heated bloom with a pair of roll
Characteristics
- Destroys the big mold structure and improves the crystal structure of material to provide excellent mechanical and physical qualities
-
- 03Hot Scarfing
- Process of removing harmful defects (cracks, shells, superficially added substances) on the surface of material that does not extinguish in the course of heating and blooming
Characteristics
- Removing decarburized layer generated during the job of heating from the surface
- Applicable to high carbon steel and alloy steel that is incapable of cold scarfing
-
- 04Large-Bar Mill
- Process of halfway rolling and manufacturing the shape and standard of final product after hot rolling
Characteristics
- Production of RB105 to 250 products and manufacture the shape of halfway rolling
-
- 05Vertical-Horizontal Mill #1
- Rolling process for manufacturing the final shape and standard of product after hot rolling
Characteristics
- Production of RB75-1165.1, SQ83-160 products
-
- 06Vertical-Horizontal Mill #2
- Rolling process for manufacturing the final shape and standard of product after hot rolling
Characteristics
- Production of RB75-1165.1, SQ83-160 products
-
- 07Cooling Bed
- Inner quality improved and straightness secured by revolving and gradually cooling a rolled product
-
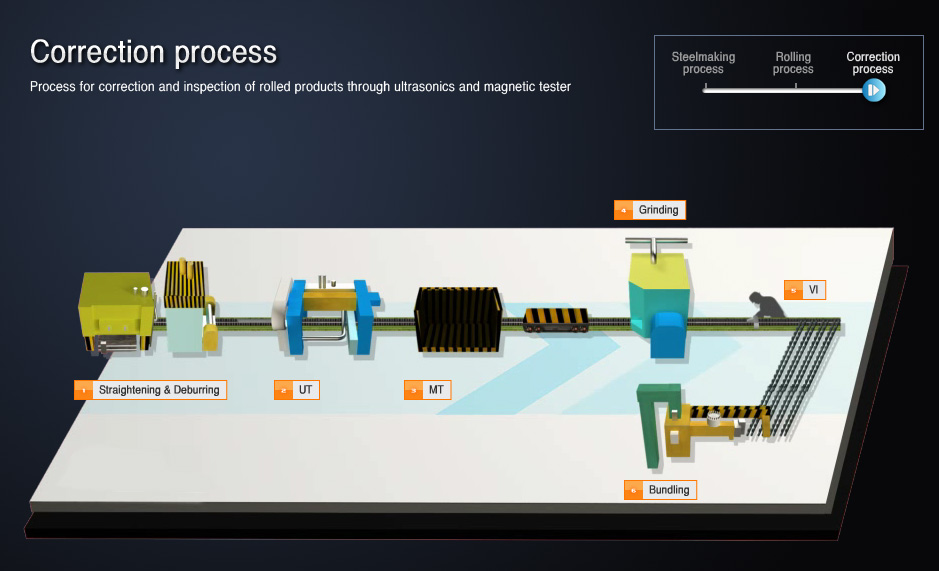
- 01Straightening&Deburring
- Straightening: equipment that secure straightness by passing a round bar through 2 rolls up and down
Deburring: equipment that removes the burr at both ends of product by fitting cutting tip with bite holder
-
- 02UT (Ultrasonic wheel probe)
- A type of NDP (non destructive testing), an equipment for discerning defects inside a product using ultrasonic waves
-
- 03MT (Magnetic particle testing unit)
- A type of NDP (non destructive testing) equipment that checks defects of the product surface by magnetizing and scattering fluorescent magnetic particles on the product
-
- 04Grinding M/C (Lapping tool)
- An equipment that removes the identified and marked surface defects via MT with grinding wheel
-
- 05VI (Testing with naked eyes)
- Final testing on the product (dimension, length, straightness, surface, etc.)
-
- 06Bundling (banding)
- An equipment for bundling products in certain units and weights